
In Cambodian, land ownership and private unit ownership (such as in condominiums) are distinct legal categories. Understanding the differences is essential for investors, developers, and property owners.
Definition
- Land Ownership: Refers to the legal right to exclusively own and possess a parcel of land, including any immovable structures attached to it.
- Private Unit Ownership: Refers to ownership of a specific unit within a co-owned building (e.g., a condominium), along with shared ownership of the building’s common areas and land.
Legal Framework
- Land Ownership: governed by the Land Law 2001, which provides for private land ownership through hard or soft titles.
- Private Unit Ownership: governed by the Law on the Co-ownership of Buildings (2010), which introduced the concept of strata title ownership in Cambodia.
Ownership Scope
- Land Ownership: Confers full rights over the land and all constructions on it. Owners have the authority to use, transfer, lease, mortgage, or develop the property.
- Private Unit Ownership: Grants exclusive ownership of an individual unit and joint ownership of common areas (e.g., corridors, elevators, parking areas, and the land beneath the building).
Foreign Ownership
- Land Ownership: Foreigners are prohibited from directly owning land. They may, however, obtain land rights through long-term leases, nominee structures, or ownership through a Cambodian-registered company with Cambodian majority shareholders.
- Private Unit Ownership: Foreigners may own up to 70% of the total units in a co-owned building (excluding ground floor units), as long as the building is registered under the co-ownership regime.
Title Documentation
- Land Ownership: Owners receive a land title certificate called certificate acknwoledgemetn of ownership over the immovable property, which it is officially registered by Ministry of Land Management Urban Planning and Construction or a soft title (recognized locally but not registered at the national level) such as letter of tranfer.
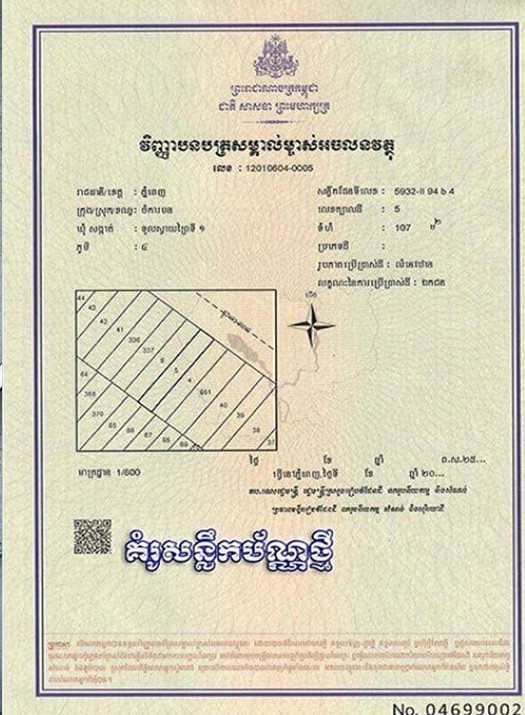
- Private Unit Ownership: Owners receive a strata title certificate, specifying ownership of the private unit and a proportionate share in the building’s common property. it official namely certificate of onwership of private unit.
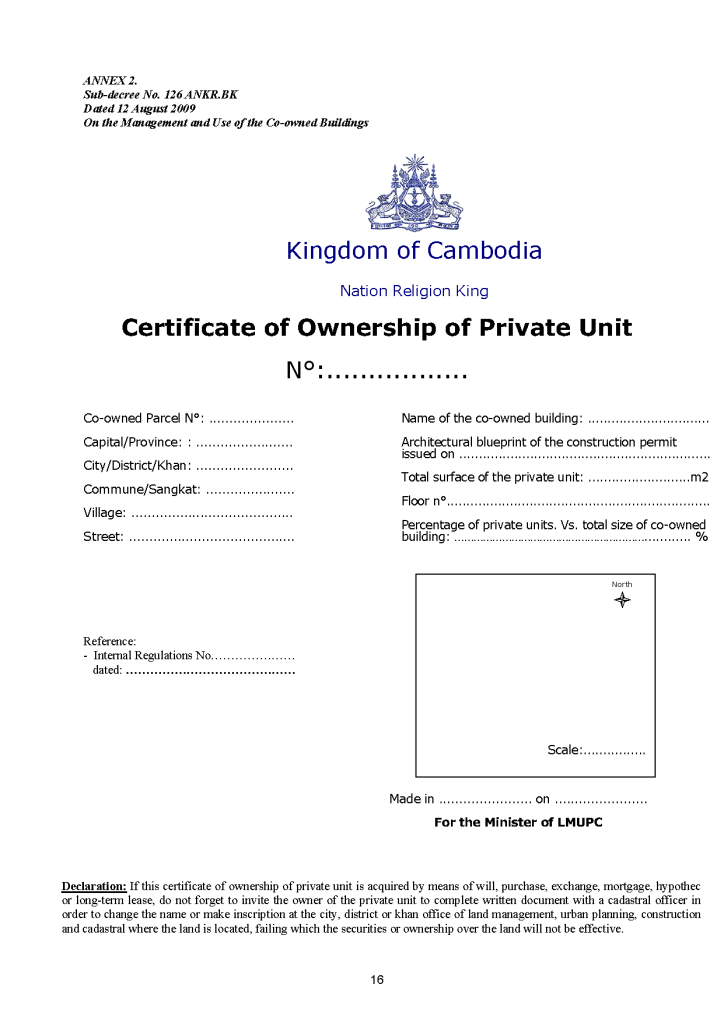
Use and Transfer Rights
- Land Ownership: Owners enjoy broad rights to use, develop, sell, lease, or transfer the land, subject to applicable laws and regulations.
- Private Unit Ownership: Unit owners can use, lease, or transfer their unit, but must comply with the co-ownership rules and maintain the shared property.

This summary is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. It is not comprehensive, and readers should seek professional legal consultation for their specific circumstances. SOPHEAPCAMBOLAW retains full ownership of this content. Unauthorized reproduction, distribution, or use of any part of this article without prior written approval is strictly prohibited.
© 2025 SOPHEAPCAMBOLAW | All Rights Reserved
សព្វទានំ ធម្មទានំ ជិនាតិ
-Buddha-
Sharing knowledge is the most worthwhile endeavor of all.

Leave a comment